Quebec teen discovers ancient Mayan ruins by studying the stars1
- From Around the Web, Space
- May 10, 2016
Scientists across the board have been blown away by Gadoury’s discovery.

Scientists across the board have been blown away by Gadoury’s discovery.

The gravitational pull of Saturn changes the amount of particles spraying from the south pole of Saturn’s active moon Enceladus at different points in its orbit.

Findings by Rutgers and other scientists could help shed light on how galaxies and their supermassive black holes form

NASA’s MESSENGER mission has unveiled the first global digital elevation model (DEM) of Mercury

The May 9 Mercury transit will occur between about 7:12 a.m. and 2:42 p.m. EDT.
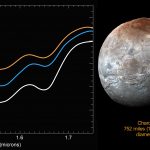
New compositional data from NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft reveal a distinct water-ice signature on the surface of Pluto’s outermost moon, Hydra.

While the full moon cannot turn people into werewolves, some people do accuse it of causing a bad night’s sleep or creating physical and mental alterations. But is there any science behind these myths?

A star like the sun has an internal driving in the form of a magnetic field that can be seen on the surface as sunspots.

Astronomers have discovered the second-strongest merger shock in clusters of galaxies ever observed.

Using data from the Solar Wind Around Pluto (SWAP) instrument from the New Horizons July 2015 flyby, scientists have for the first time observed the material coming off of Pluto’s atmosphere and studied how it interacts with the solar wind, leading to yet another “Pluto surprise.”



