Scientists digitally reconstruct skulls of dinosaurs in fossilised eggs0
- Ancient Archeology, From Around the Web
- April 11, 2020
Research on Massospondylus carinatus embryos sheds new light on animals’ development

Research on Massospondylus carinatus embryos sheds new light on animals’ development
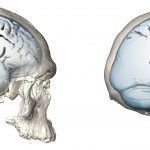
The Paleoneurobiology Group of the Centro Nacional de Investigación sobre la Evolución Humana (CENIEH), led by Emiliano Bruner, has just published a morphological analysis of the brains of Neanderthals and modern humans in the Journal of Human Evolution, whose results suggest that the more rounded shape of modern human brains is due in part to larger and bulgier parietal lobes, on average.
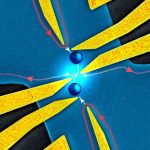
Some types of anyons may eventually be useful for building better quantum computers

BepiColombo needs our planet’s help

New Zealand Prime Minister Jacinda Ardern has declared the Easter Bunny to be an essential worker in her country, stating that the rabbit can go about its mysterious business this Sunday as usual, despite a nationwide lockdown.

Detailed image taken by Event Horizon Telescope of black hole 5bn light years away
Scientists have revisited one of the most iconic images taken with the Hubble Space Telescope, revealing incredible details in infrared light.

Astronomers using the CARMENES spectrograph at Calar Alto Observatory in Spain have discovered a super-Earth exoplanet orbiting an M-dwarf star in the binary system Gliese 338. The newfound planet orbits on the inner edge of the habitable zone and is much more massive than Earth.

When it comes to deciphering our ancient family tree, DNA from fossils is the new gold standard. But after about half a million years, even the best-preserved DNA degrades into illegibility, leaving the story of our early evolution shrouded in mystery. A new study of proteins taken from the tooth of an enigmatic human ancestor reveals their rough place in the family tree—and shows how ancient proteins can push beyond the limits of DNA.



