A supernova’s delayed reappearance could pin down how fast the universe expands0
- From Around the Web, Space
- September 13, 2021
The catch: We have to wait until about 2037 for an answer

The catch: We have to wait until about 2037 for an answer

Researchers have found that black holes may exert pressure on their surroundings. The discovery made by a team of astronomers in the U.K. builds on a theory posited by Stephen Hawking in 1974, which suggests black holes give off thermal radiation.
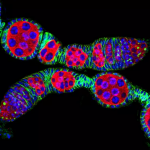
The findings suggest a way to rescue “doomed” animal hybrids.

A billion years have vanished from the geological record – and over 152 years after this was first discovered, scientists can’t agree on why.

A full-on impact by this giant likely would have broken the already unstable ice shelf.

Astronomers have discovered that dying white dwarf stars can burn nuclear fuel in their outer shells, prolonging their lives. The discovery made using the Hubble Space Telescope runs contrary to the current view of white dwarfs as just slowly cooling inert star cores.

It was getting late and the team of paleontologists excavating a previously unexplored outcrop of the Burgess Shale was ready to call it a day. A camera crew filming the dig in Kootenay National Park had already packed it in.

2021 PJ1, a near-Earth asteroid between 20 and 30 m (66-98 feet) across, safely flew past Earth on August 14, 2021 at a distance of over 1.7 million km (1 million miles). The approach was historic, marking the 1,000th near-Earth asteroid to be observed by NASA’s planetary radar in just over 50 years.

The rocket nailed its liftoff, but started cartwheeling mid-air before perishing in an explosive fireball

Prof Paul Davies suggests viruses may form vital part of ecosystems on other planets



