Researchers Drill Deep Into One of the Most Important Antarctica Glaciers0
- Ancient Archeology, From Around the Web, Science & Technology
- January 30, 2020
The melting of Thwaites Glacier already accounts for 4% of global sea-level rise.

The melting of Thwaites Glacier already accounts for 4% of global sea-level rise.

Scientists from Washington University, St. Louis, Caltech and the University of Chicago have found presolar grains — tiny bits of solid interstellar material formed before the Sun was born — in Curious Marie, a sample of the famous Allende meteorite.

Local people called them “Ciampate del Diavolo” or the devil’s trail, as only a supernatural entity could leave its footprints in apparent solid rocks. Discovered in 2001, for archaeologists the devil’s trails site near the Italian town of Roccamonfina is a rare example of humanoid footprints preserved in volcanic rocks.
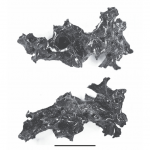
A man who died in Herculaneum during the historic Vesuvius eruption was found with an exploded skull and glass-like brain tissue.
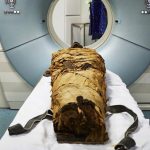
The replica reveals what the ancient Egyptian’s voice might have sounded like

Extensive water channels built by indigenous Australians thousands of years ago to trap and harvest eels for food have been revealed after wildfires burned away thick vegetation in the state of Victoria.

Yarrabubba Crater was blasted out by an asteroid or comet about 2.23 billion years ago.

Marine die-offs after the impact may have created opportunities for the life that survived around the globe, new data reveal.

San Diego Natural History Museum paleontologist describes a dinosaur that is new to science, offers view into dinosaur-bird evolution

A microorganism scooped up in deep-sea mud off Japan’s coast has helped scientists unlock the mystery of one of the watershed evolutionary events for life on Earth: the transition from the simple cells that first colonized the planet to complex cellular life – fungi, plants and animals including people.



