Solar Minimum is becoming very deep indeed.
Source: Spaceweather.com
Over the weekend, the sun set a Space Age record for spotlessness. So far in 2019, the sun has been without sunspots for more than 271 days, including the last 34 days in a row. Since the Space Age began, no other year has had this many blank suns.
The previous record-holder was the year 2008, when the sun was blank for 268 days. That was during the epic Solar Minimum of 2008-2009, formerly the deepest of the Space Age. Now 2019 has moved into first place.
Solar Minimum is a normal part of the 11-year sunspot cycle. The past two (2008-2009 and 2018-2019) have been long and deep, making them “century-class” Minima. To find a year with more blank suns, you have to go back to 1913, which had 311 spotless days.
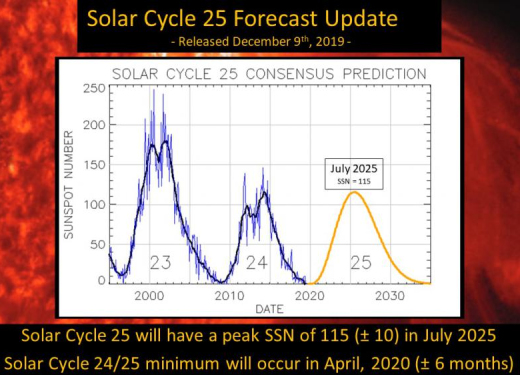
Last week, the NOAA/NASA Solar Cycle Prediction Panel issued a new forecast. Based on a variety of predictive techniques, they believe that the current Solar Minimum will reach its deepest point in April 2020 (+/- 6 months) followed by a new Solar Maximum in July 2025. This means that low sunspot counts and weak solar activity could continue for some time to come.
Solar Minimum definitely alters the character of space weather. Solar flares and geomagnetic storms subside, making it harder to catch Northern Lights at mid-latitudes. Space weather grows “quiet.” On the other hand, cosmic rays intensify. The sun’s weakening magnetic field allows more particles from deep space into the solar system, boosting radiation levels in Earth’s atmosphere. Indeed, this is happening now with atmospheric cosmic rays at a 5-year high and flirting with their own Space Age record. It’s something to think about the next time you step on an airplane.
Source: Spaceweather.com





























Leave a Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.